One of Brazil’s top scientists, Eneas Salati, once said, “The best thing you could do for the Amazon rainforest is to blow up all the roads.” He wasn’t joking. And he had a point.
In an article published on 10 April in Nature, my colleagues and I show that illicit, often out-of-control road building is imperilling forests in Indonesia, Malaysia and Papua New Guinea. The roads we’re studying do not appear on legitimate maps. We call them “ghost roads”.
What’s so bad about a road? A road means access. Once roads are bulldozed into rainforests, illegal loggers, miners, poachers and landgrabbers arrive. Once they get access, they can destroy forests, harm native ecosystems and even drive out or kill indigenous peoples. This looting of the natural world robs cash-strapped nations of valuable natural resources. Indonesia, for instance, loses around A$1.5 billion (US$979.5 million) each year solely to timber theft.
All nations have some unmapped or unofficial roads, but the situation is especially bad in biodiversity-rich developing nations, where roads are proliferating at the fastest pace in human history.
For this study, my PhD student Jayden Engert and I worked with Australian and Indonesian colleagues to recruit and train more than 200 volunteers.
This workforce then spent some 7,000 hours hand-mapping roads, using fine-scale satellite images from Google Earth. Our team of volunteers mapped roads across more than 1.4 million square kilometres of the Asia-Pacific region.
As the results rolled in, we realised we had found something remarkable. For starters, unmapped ghost roads seemed to be nearly everywhere. In fact, when comparing our findings to two leading road databases, OpenStreetMap and the Global Roads Inventory Project, we found ghost roads in these regions to be 3 to 6.6 times longer than all mapped roads put together.
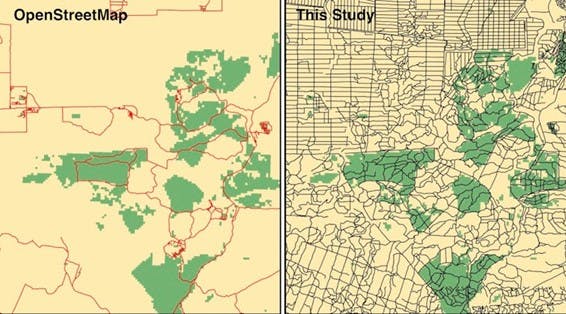
Mapped roads in northeastern Borneo using a leading road database, OpenStreetMap (left), and with the ghost roads identified in this study added (right). Image: Bill Laurance/ CC BY-NC-ND
When ghost roads appear, local deforestation soars – usually immediately after the roads are built. We found the density of roads was by far the most important predictor of forest loss, outstripping 38 other variables. No matter how one assesses them, roads are forest killers.
What makes this situation uniquely dangerous for conservation is that the roads are growing fast while remaining hidden and outside government control.
Not even parks and protected areas in the Asia-Pacific are fully safe from illegal roads.
But safeguarding parks does have an effect. In protected areas, we found only one-third as many roads compared with nearby unprotected lands.
The bad news is that when people do build roads inside protected areas, it leads to about the same level of forest destruction compared to roads outside them.
Our findings suggest it is essential to limit roads and associated destruction inside protected areas. If we can find these roads using satellite images, authorities can too. Once an illegal road is found, it can be destroyed or at least mapped and managed as a proper legal road.
Keeping existing protected areas intact is especially urgent, given more than 3,000 protected areas have already been downsized or degraded globally for new roads, mines and local land-use pressures.
The human footprint of hidden roads
The impact we have on the planet differs from place to place. To gauge how much impact we’re having, researchers use the human footprint index, which brings together data on human activities such as roads and other infrastructure, land-uses, illumination at night from electrified settlements and so on. You can use the index to make heat-maps showing where human impacts are most or least pronounced.
We fed our ghost road discoveries into the index and compared two versions for eastern Borneo, one without ghost road information and one with it. The differences are striking.
When ghost roads are included in mapping the human impact on eastern Borneo, areas with “very high” human disturbance double in size, while the areas of “low” disturbance are halved.
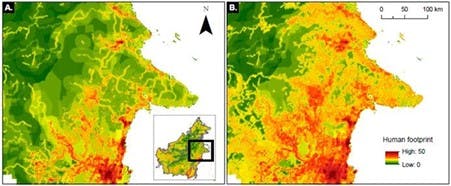
This is what the human footprint heatmap for east-central Borneo looks like, first without ghost roads (A) and second with ghost roads included (B). Image: Bill Laurance/ CC BY-NC-ND
Researchers investigating other biodiversity-rich developing regions such as Amazonia and the Congo Basin have found many illegal unmapped roads in those locales too.
Ghost roads, it seems, are an epidemic. Worse, these roads can be actively encouraged by aggressive infrastructure-expansion schemes — most notably China’s Belt and Road Initiative, now active in more than 150 nations.
For now, mapping ghost roads is very labour-intensive. You might think AI could do this better, but that’s not yet true – human eyes can still outperform image-recognition AI software for mapping roads.
At our current rate of work, visually mapping all roads – legal and illicit – across Earth’s land surface just once would require around 640,000 person-hours (or 73 person-years) to complete.
Given these challenges, our group and other researchers are now testing AI methods, hoping to provide accurate, global-scale mapping of ghost roads in close to real time. Nothing else can keep pace with the contemporary avalanche of proliferating roads.
We urgently need to be able to map the world’s roads accurately and often. Once we have this information, we can make it public so that authorities, NGOs and researchers involved in forest protection can see what’s happening.
Without this vital information, we’re flying blind. Knowing what’s happening in the rainforest is the first step to stopping the destruction.
William Laurance is a distinguished research professor and Australian laureate at James Cook University. This article was originally published on The Conversation.









